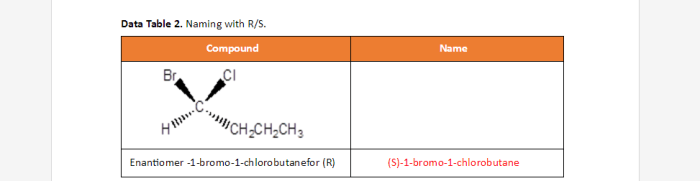
S 1 bromo 1 chlorobutane – 1-Bromo-1-chlorobutane, a versatile organic compound, holds a prominent position in various industries and research endeavors. With its unique chemical properties and reactivity, it plays a crucial role in synthesis, pharmaceuticals, and more. Let’s delve into the fascinating world of 1-bromo-1-chlorobutane, exploring its properties, applications, and environmental implications.
This compound, characterized by its molecular formula C4H8BrCl, possesses a molecular structure that influences its physical and chemical behavior. Its boiling point, melting point, and density are all essential parameters to consider when handling and using 1-bromo-1-chlorobutane.
Chemical Properties
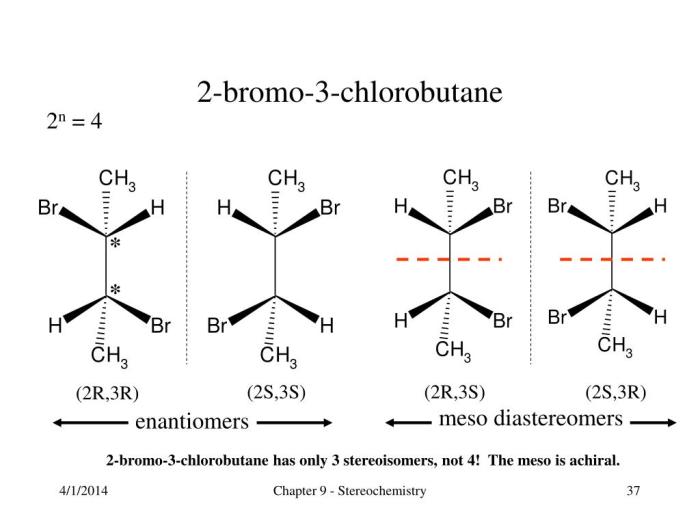
1-bromo-1-chlorobutane is an organic compound with the molecular formula C 4H 8BrCl. It is a colorless liquid with a boiling point of 156-157 °C, a melting point of -73 °C, and a density of 1.49 g/cm 3. It is soluble in organic solvents such as ether and chloroform, but insoluble in water.
Physical Properties
- Boiling point: 156-157 °C
- Melting point: -73 °C
- Density: 1.49 g/cm 3
- Solubility: Soluble in organic solvents, insoluble in water
Chemical Reactivity
1-bromo-1-chlorobutane is a reactive compound that can undergo a variety of chemical reactions. It is a good electrophile, and it can react with nucleophiles to form a variety of products. It can also undergo elimination reactions to form alkenes. The most common reactions of 1-bromo-1-chlorobutane are:
- Nucleophilic substitution reactions
- Elimination reactions
- Addition reactions
Reactivity and Reactions: S 1 Bromo 1 Chlorobutane
-bromo-1-chlorobutane is a reactive compound that can undergo a variety of reactions. The most common types of reactions are nucleophilic substitution and elimination reactions.
Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions
In a nucleophilic substitution reaction, a nucleophile (a species with a lone pair of electrons) attacks the electrophilic carbon atom in 1-bromo-1-chlorobutane, displacing the leaving group (bromine or chlorine). The product of the reaction is a new compound in which the nucleophile has replaced the leaving group.One
example of a nucleophilic substitution reaction is the reaction of 1-bromo-1-chlorobutane with sodium hydroxide. In this reaction, the hydroxide ion (OH-) acts as the nucleophile and attacks the electrophilic carbon atom, displacing the bromide ion (Br-). The product of the reaction is 1-butanol.
Elimination Reactions
In an elimination reaction, a base removes a proton from a carbon atom adjacent to the electrophilic carbon atom in 1-bromo-1-chlorobutane, causing the leaving group to be eliminated. The product of the reaction is an alkene.One example of an elimination reaction is the reaction of 1-bromo-1-chlorobutane with potassium tert-butoxide.
The organic compound s 1 bromo 1 chlorobutane, also known as 1-bromo-1-chlorobutane, has a molecular formula of C4H8BrCl. For students studying APUSH Period 6, understanding key terms is crucial. By delving into apush period 6 key terms , one can grasp the complexities of this historical era.
Returning to s 1 bromo 1 chlorobutane, its chemical structure and properties are essential for comprehending organic chemistry.
In this reaction, the tert-butoxide ion (t-BuO-) acts as the base and removes a proton from the carbon atom adjacent to the electrophilic carbon atom, causing the bromide ion (Br-) to be eliminated. The product of the reaction is 1-butene.
Synthesis and Production
-bromo-1-chlorobutane can be synthesized through various methods, including:
- Addition of hydrogen bromide (HBr) to 1,3-butadiene
- Addition of chlorine (Cl2) to 1-bromobutane
- Reaction of 1-butanol with phosphorus tribromide (PBr3) and then with thionyl chloride (SOCl2)
Laboratory-Scale Synthesis
One common laboratory-scale synthesis method involves the addition of HBr to 1,3-butadiene:
- In a round-bottom flask equipped with a condenser, dissolve 1,3-butadiene in an inert solvent such as dichloromethane.
- Slowly add HBr gas to the solution while stirring vigorously.
- Continue stirring for several hours or until the reaction is complete.
- Wash the reaction mixture with water and brine.
- Dry the organic layer over anhydrous sodium sulfate.
- Distill the product to obtain pure 1-bromo-1-chlorobutane.
Industrial-Scale Production
On an industrial scale, 1-bromo-1-chlorobutane is typically produced by the addition of chlorine to 1-bromobutane. This reaction is carried out in a continuous reactor at elevated temperatures and pressures.
1-bromobutane + Cl2 → 1-bromo-1-chlorobutane + HCl
The product is then purified by distillation to remove any unreacted starting materials or byproducts.
Applications and Uses
-bromo-1-chlorobutane finds applications in various industries due to its unique properties. It is primarily utilized as a solvent, intermediate, and alkylating agent.
As a Solvent
-bromo-1-chlorobutane is a versatile solvent employed in the extraction and purification of organic compounds. Its ability to dissolve a wide range of substances makes it suitable for use in industries such as pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and chemical manufacturing.
As an Intermediate
In the chemical industry, 1-bromo-1-chlorobutane serves as an intermediate in the synthesis of other organic compounds. It is commonly used in the production of pharmaceuticals, agrochemicals, and dyes.
As an Alkylating Agent
-bromo-1-chlorobutane’s alkylating properties allow it to be used as a reagent in organic synthesis. It can introduce butyl groups into various organic molecules, enabling the creation of new compounds with tailored properties.
Potential Applications in New Technologies
Ongoing research explores the potential of 1-bromo-1-chlorobutane in emerging technologies. Its unique reactivity and versatility hold promise for applications in fields such as nanotechnology, materials science, and energy storage.
Safety and Hazards
1-bromo-1-chlorobutane is a highly reactive and potentially hazardous chemical. It is important to understand the potential risks associated with handling, storing, and disposing of this compound to ensure safety.
Exposure to 1-bromo-1-chlorobutane can cause various health effects. Inhalation of its vapors can irritate the respiratory tract, leading to coughing, shortness of breath, and chest pain. Skin contact can result in irritation, redness, and blistering. Eye exposure can cause severe irritation, redness, and even corneal damage.
Proper Handling
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, goggles, and a respirator, when handling 1-bromo-1-chlorobutane.
- Work in a well-ventilated area to minimize exposure to vapors.
- Avoid contact with skin, eyes, and clothing.
- Keep containers tightly sealed when not in use.
Storage
- Store 1-bromo-1-chlorobutane in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area away from heat, light, and incompatible materials.
- Keep containers tightly closed to prevent leakage and contamination.
- Store in a designated chemical storage area, separate from food and other incompatible substances.
Disposal, S 1 bromo 1 chlorobutane
- Dispose of 1-bromo-1-chlorobutane according to local, state, and federal regulations.
- Do not pour down the drain or dispose of in the trash.
- Incineration is the preferred method of disposal, as it destroys the compound and prevents its release into the environment.
Safety Guidelines and Regulations
There are specific safety guidelines and regulations in place for working with 1-bromo-1-chlorobutane. These regulations may vary depending on the jurisdiction, but generally include:
- Requirements for proper ventilation, PPE, and emergency response plans.
- Restrictions on storage and disposal practices.
- Training and certification requirements for personnel handling the chemical.
It is essential to comply with all applicable safety guidelines and regulations to minimize the risks associated with working with 1-bromo-1-chlorobutane.
Environmental Impact
-bromo-1-chlorobutane has the potential to cause adverse environmental effects due to its persistence, biodegradability, and toxicity.
This compound is considered persistent in the environment, meaning it can remain for extended periods without breaking down. Its resistance to biodegradation makes it difficult for natural processes to remove it from the environment.
Toxicity
-bromo-1-chlorobutane exhibits toxicity to aquatic organisms. Exposure to this compound can cause adverse effects on fish, invertebrates, and algae. Studies have shown that it can impair growth, reproduction, and survival of aquatic species.
The presence of 1-bromo-1-chlorobutane in water bodies can disrupt ecosystems and alter the balance of aquatic communities. Its persistence and toxicity pose significant concerns for the health of aquatic environments.
Q&A
What are the key chemical properties of 1-bromo-1-chlorobutane?
1-Bromo-1-chlorobutane is a colorless liquid with a pungent odor. It has a molecular formula of C4H8BrCl, a boiling point of 156-158 °C, a melting point of -95 °C, and a density of 1.28 g/mL.
What types of reactions can 1-bromo-1-chlorobutane undergo?
1-Bromo-1-chlorobutane can undergo a variety of reactions, including nucleophilic substitution, elimination, and addition reactions. Nucleophilic substitution reactions are the most common, and they involve the replacement of the bromine or chlorine atom with a nucleophile.
How is 1-bromo-1-chlorobutane synthesized?
1-Bromo-1-chlorobutane can be synthesized by a variety of methods, including the reaction of 1-butanol with hydrogen bromide and chlorine gas. It can also be synthesized by the reaction of 1-chlorobutane with bromine.
What are the applications of 1-bromo-1-chlorobutane?
1-Bromo-1-chlorobutane is used as a solvent, an intermediate in the synthesis of other chemicals, and an alkylating agent. It is also used in the production of pharmaceuticals, pesticides, and dyes.
What are the potential hazards of 1-bromo-1-chlorobutane?
1-Bromo-1-chlorobutane is a flammable and toxic chemical. It can cause skin and eye irritation, and it is harmful if inhaled or ingested. It is important to handle and store 1-bromo-1-chlorobutane with care.