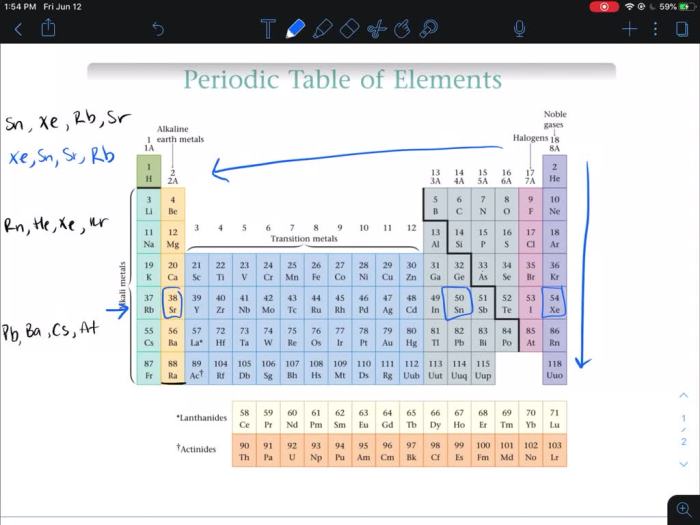
Rank the following elements by increasing atomic radius: a journey into the fascinating world of atomic structure, where we unravel the intricate relationship between atomic number and atomic radius, exploring the periodic trends that govern the size of atoms and their profound impact on chemical properties and applications.
Delving into the depths of atomic radius, we will uncover the experimental and theoretical methods employed to determine the size of atoms, critically examining their accuracy and limitations. Furthermore, we will dissect the factors that influence atomic radius, revealing how these factors can be harnessed to predict atomic size and unravel the mysteries of chemical behavior.
1. Elements by Increasing Atomic Radius
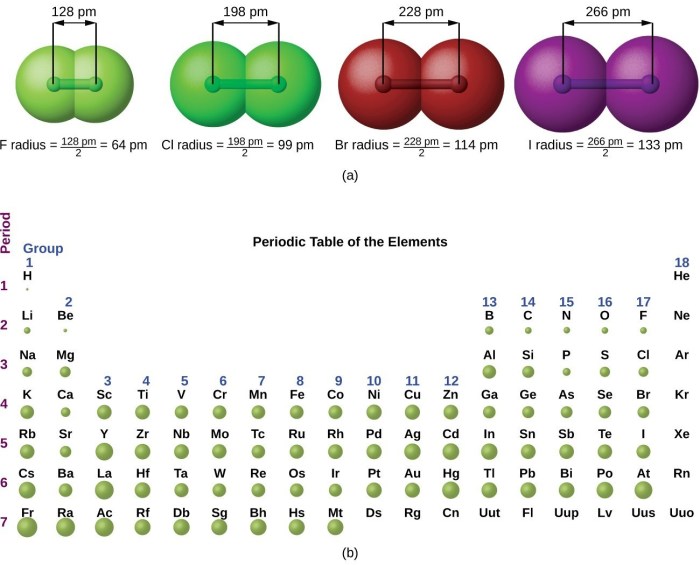
Atomic radius is a measure of the distance from the nucleus to the outermost electron shell of an atom. It is an important property that affects many chemical and physical properties of elements.
The atomic radius generally increases down a group and decreases across a period in the periodic table. This is because the number of electron shells increases down a group, making the atoms larger. Across a period, the number of protons in the nucleus increases, which attracts the electrons more strongly and makes the atoms smaller.
Methods for Determining Atomic Radius, Rank the following elements by increasing atomic radius
There are several methods that can be used to determine the atomic radius of an element.
- Experimental methodsinvolve measuring the distance between atoms in a crystal lattice. This can be done using X-ray diffraction or neutron scattering.
- Theoretical methodsinvolve calculating the atomic radius using quantum mechanics. These methods are based on the Schrödinger equation and take into account the interactions between the electrons in the atom.
The accuracy of different methods for determining atomic radius varies. Experimental methods are generally more accurate than theoretical methods, but they can only be used for elements that form crystals. Theoretical methods can be used for all elements, but they are less accurate.
Factors Affecting Atomic Radius
The atomic radius of an element is affected by several factors, including:
- Number of electron shells: The more electron shells an atom has, the larger the atomic radius.
- Number of electrons: The more electrons an atom has, the larger the atomic radius.
- Nuclear charge: The greater the nuclear charge, the smaller the atomic radius.
These factors can be used to predict the atomic radius of an element. For example, an element with a large number of electron shells and a small number of electrons will have a large atomic radius. An element with a small number of electron shells and a large number of electrons will have a small atomic radius.
Applications of Atomic Radius
The atomic radius of an element is used in a variety of applications, including:
- Predicting chemical properties: The atomic radius can be used to predict the chemical properties of an element. For example, elements with large atomic radii are more likely to be reactive than elements with small atomic radii.
- Materials science: The atomic radius is used in materials science to design new materials with specific properties. For example, materials with large atomic radii are often used as insulators, while materials with small atomic radii are often used as conductors.
The atomic radius is a fundamental property of elements that has a wide range of applications in chemistry and materials science.
Frequently Asked Questions: Rank The Following Elements By Increasing Atomic Radius
What is atomic radius?
Atomic radius is a measure of the size of an atom, defined as the distance from the nucleus to the outermost electron shell.
How does atomic number affect atomic radius?
Atomic number, which represents the number of protons in an atom, has an inverse relationship with atomic radius. As atomic number increases, the number of electrons also increases, leading to a stronger attraction between the nucleus and the electrons, resulting in a smaller atomic radius.
What are the periodic trends in atomic radius?
Atomic radius generally increases down a group (column) in the periodic table and decreases across a period (row). This is due to the increasing number of electron shells and the shielding effect of inner electrons.