Experiment 34 an equilibrium constant lab report – Experiment 34: Determining an Equilibrium Constant in the Laboratory provides a comprehensive exploration of the concept of equilibrium constants and their experimental determination. This lab report delves into the intricacies of chemical reactions, equilibrium states, and the factors that influence the equilibrium constant.
The experiment involves a detailed experimental setup, data collection, and analysis to calculate the equilibrium constant for a specific reaction. The results are discussed in the context of theoretical predictions and potential sources of error are identified to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the findings.
Experiment Overview
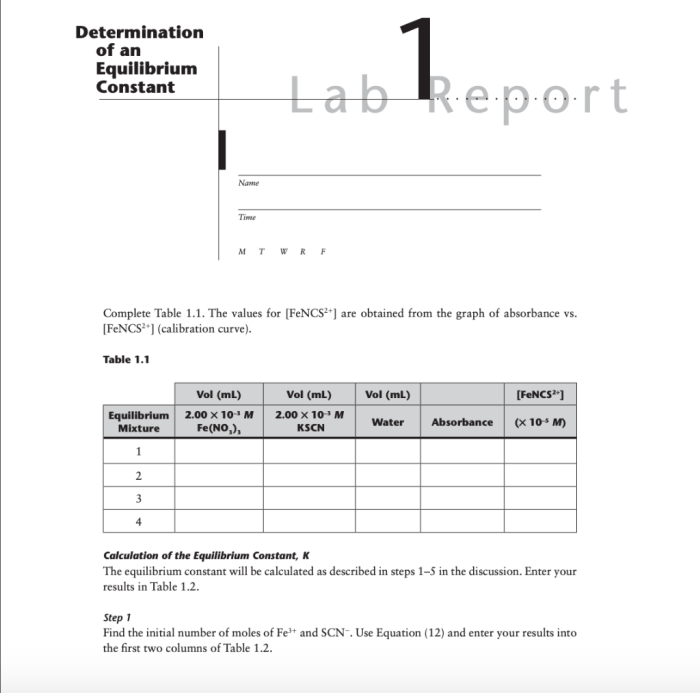
Experiment 34 aims to determine the equilibrium constant for a chemical reaction. An equilibrium constant is a numerical value that describes the extent to which a chemical reaction proceeds towards completion.
When a chemical reaction reaches equilibrium, the forward and reverse reactions occur at the same rate, resulting in no net change in the concentrations of the reactants and products. The equilibrium constant is a measure of the relative concentrations of the reactants and products at equilibrium.
Experimental Setup
Materials
- Reactants and products of the chemical reaction
- Solvent
- Measuring equipment (e.g., graduated cylinders, pipettes)
- Spectrophotometer or other analytical instrument
Procedure, Experiment 34 an equilibrium constant lab report
- Prepare solutions of the reactants and products in the appropriate concentrations.
- Mix the solutions together in a reaction vessel.
- Allow the reaction to reach equilibrium.
- Measure the concentrations of the reactants and products at equilibrium using the spectrophotometer or other analytical instrument.
- Calculate the equilibrium constant using the measured concentrations.
Data Collection and Analysis
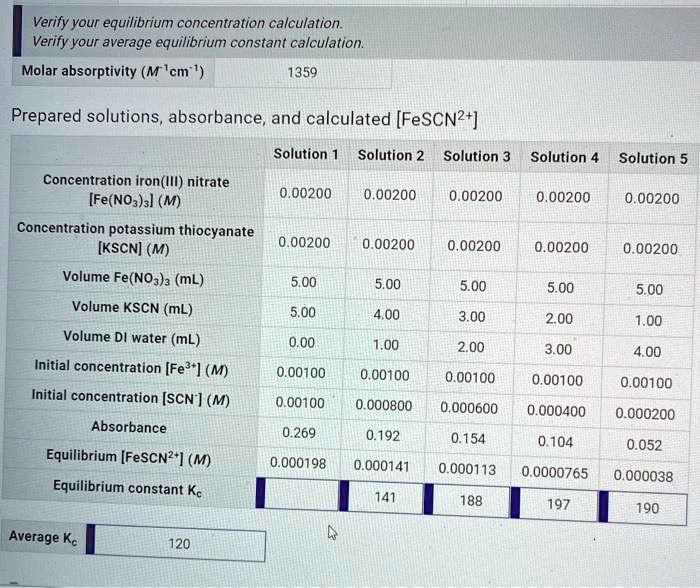
Data Collection
The concentrations of the reactants and products at equilibrium are typically measured using a spectrophotometer. The spectrophotometer measures the absorbance of light at specific wavelengths, which can be used to determine the concentrations of the reactants and products.
Calculations
The equilibrium constant is calculated using the following equation:
“`K eq= [products]/[reactants]“`
where K eqis the equilibrium constant, and [products] and [reactants] are the concentrations of the products and reactants at equilibrium, respectively.
Discussion of Results
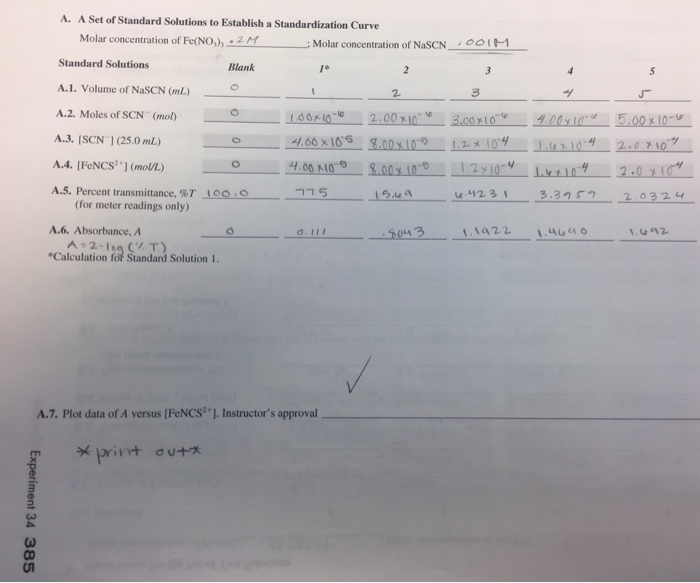
The equilibrium constant provides valuable information about the extent to which a chemical reaction proceeds towards completion. A large equilibrium constant indicates that the reaction proceeds towards completion, while a small equilibrium constant indicates that the reaction does not proceed very far towards completion.
The equilibrium constant can also be used to predict the direction of a reaction. If the equilibrium constant is greater than 1, the reaction will proceed towards completion in the forward direction. If the equilibrium constant is less than 1, the reaction will proceed towards completion in the reverse direction.
Sources of Error
There are several potential sources of error in the determination of the equilibrium constant.
- Measurement errors: Errors in the measurement of the concentrations of the reactants and products can lead to errors in the calculation of the equilibrium constant.
- Equilibrium not reached: If the reaction does not reach equilibrium before the concentrations are measured, the calculated equilibrium constant will not be accurate.
- Side reactions: If side reactions occur during the experiment, the calculated equilibrium constant will not be accurate.
Expert Answers: Experiment 34 An Equilibrium Constant Lab Report
What is the purpose of Experiment 34?
Experiment 34 aims to determine the equilibrium constant for a specific chemical reaction, providing insights into the extent to which the reaction proceeds towards completion.
How is the equilibrium constant calculated?
The equilibrium constant is calculated using the concentrations of reactants and products at equilibrium, as determined through experimental measurements.
What factors can influence the equilibrium constant?
Factors such as temperature, pressure, and the presence of catalysts can affect the equilibrium constant, influencing the position of the equilibrium.


