Embark on a scientific odyssey with our Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes Worksheet Answer Key, a comprehensive guide that unravels the intricate world of cells. Delve into the fundamental distinctions between these two cellular realms, unlocking the secrets of life’s building blocks.
Discover the structural marvels of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, from the enigmatic nucleoid to the powerhouse mitochondria. Explore their diverse metabolic pathways, unraveling the intricate dance of photosynthesis and respiration. Witness the fascinating reproductive strategies employed by these cellular wonders, from binary fission to the elegance of mitosis.
Overview of Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
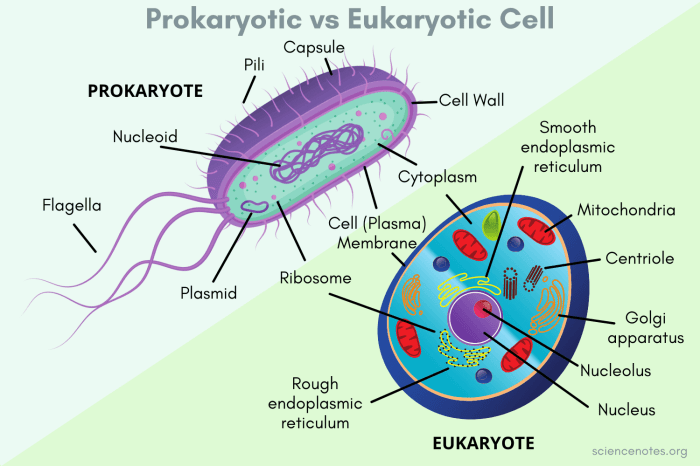
Prokaryotes and eukaryotes are the two main types of cells. Prokaryotes are simpler and smaller than eukaryotes, and they do not have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryotes, on the other hand, have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, and they are more complex and larger than prokaryotes.
The table below compares the key differences between prokaryotes and eukaryotes:
| Characteristic | Prokaryotes | Eukaryotes |
|---|---|---|
| Size | 0.1-5.0 μm | 10-100 μm |
| Shape | Coccus, bacillus, spirillum | Variable |
| Nucleus | No | Yes |
| Membrane-bound organelles | No | Yes |
| Ribosomes | 70S | 80S |
| Reproduction | Binary fission | Mitosis or meiosis |
Prokaryotic Cell Structure

Prokaryotic Cell Membrane
The prokaryotic cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer that surrounds the cell and protects its contents. It also regulates the passage of materials into and out of the cell.
Cytoplasm
The cytoplasm is the gel-like substance that fills the cell. It contains the cell’s organelles, which are small structures that perform specific functions.
Ribosomes
Ribosomes are small organelles that are responsible for protein synthesis.
Nucleoid
The nucleoid is the region of the cell that contains the cell’s DNA.
Eukaryotic Cell Structure
Eukaryotic Cell Membrane
The eukaryotic cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer that surrounds the cell and protects its contents. It also regulates the passage of materials into and out of the cell.
Nucleus
The nucleus is a membrane-bound organelle that contains the cell’s DNA.
Endoplasmic Reticulum
The endoplasmic reticulum is a network of membranes that folds and transports proteins.
Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus is a stack of flattened membranes that modifies and packages proteins.
Mitochondria, Prokaryotes and eukaryotes worksheet answer key
Mitochondria are organelles that produce energy for the cell.
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Metabolism: Prokaryotes And Eukaryotes Worksheet Answer Key

Prokaryotes and eukaryotes use different metabolic processes to obtain energy. Prokaryotes can use a variety of organic and inorganic compounds as energy sources, while eukaryotes can only use organic compounds as energy sources.
Prokaryotes can also use photosynthesis to convert light energy into chemical energy, while eukaryotes cannot.
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Reproduction

Prokaryotes reproduce by binary fission, while eukaryotes reproduce by mitosis or meiosis.
Binary Fission
Binary fission is a type of asexual reproduction in which a cell divides into two identical daughter cells.
Mitosis
Mitosis is a type of cell division that produces two identical daughter cells.
Meiosis
Meiosis is a type of cell division that produces four daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
FAQ Corner
What is the primary distinction between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
Prokaryotes lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, while eukaryotes possess both.
How do prokaryotes reproduce?
Prokaryotes reproduce through binary fission, a simple division of the cell into two identical daughter cells.
What is the role of mitochondria in eukaryotic cells?
Mitochondria are the energy powerhouses of eukaryotic cells, responsible for generating ATP through cellular respiration.