Left lateral decubitus position x ray – The left lateral decubitus position x-ray is a crucial diagnostic tool that provides valuable insights into thoracic and abdominal structures. This comprehensive guide explores the standard procedure for positioning a patient in the left lateral decubitus position, identifies anatomical landmarks visible in this position, and discusses its diagnostic applications, technical considerations, reporting, and interpretation.
Proper patient positioning is essential for accurate x-ray imaging. The left lateral decubitus position allows for the visualization of specific anatomical details that may not be visible in other positions, making it particularly useful in diagnosing pleural effusions, pneumothorax, and other thoracic abnormalities.
Positioning Techniques
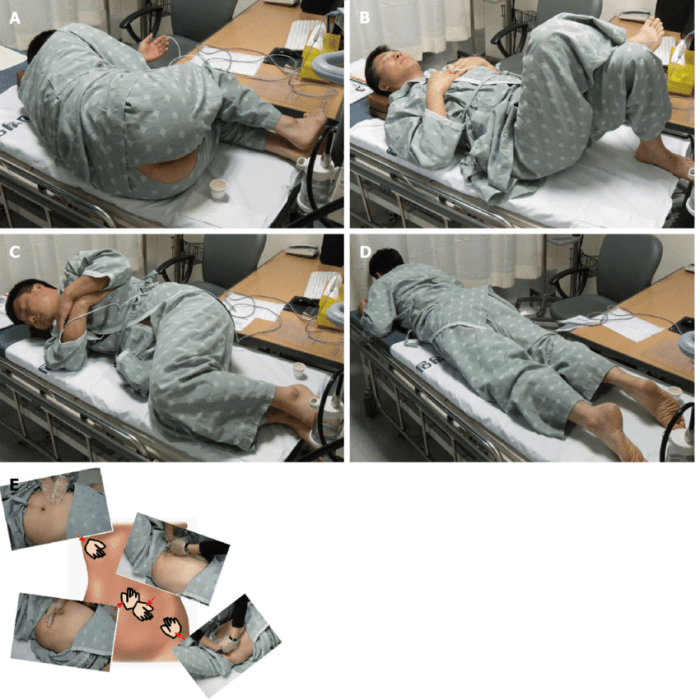
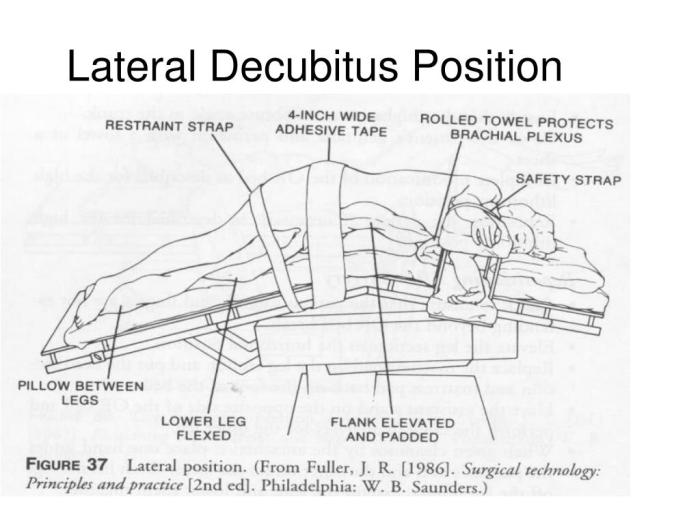
The standard procedure for positioning a patient in the left lateral decubitus position involves the following steps:
- The patient is positioned on their left side, with their right arm extended overhead and their left arm resting on their left thigh.
- The patient’s head is supported by a pillow, and their neck is extended slightly.
- The patient’s legs are flexed at the knees and hips, with their right leg slightly more flexed than their left.
- The patient’s spine is straight, and their shoulders are relaxed.
Proper patient positioning is essential for accurate X-ray imaging. Incorrect positioning can lead to distorted images, which can make it difficult to diagnose medical conditions.
Positioning aids, such as pillows, sandbags, and straps, can be used to maintain patient stability and ensure proper positioning.
Anatomical Landmarks
The left lateral decubitus position X-ray reveals several important anatomical landmarks, including:
- The heart and mediastinum
- The lungs and pleura
- The diaphragm
- The stomach and intestines
- The kidneys and ureters
These landmarks can be used to evaluate the size, shape, and position of these structures, as well as to identify any abnormalities.
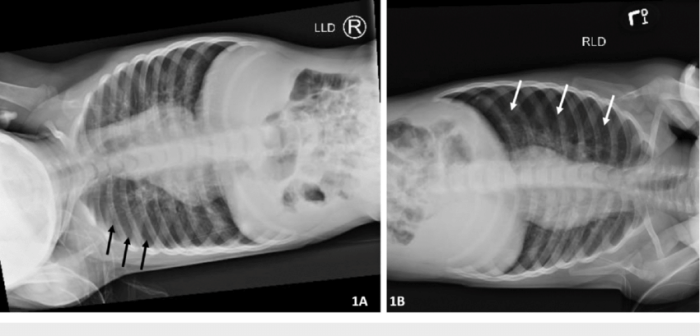
The left lateral decubitus position can reveal specific anatomical details that are not visible in other positions. For example, this position can be used to detect pleural effusions, which are collections of fluid in the pleural space.
Diagnostic Applications: Left Lateral Decubitus Position X Ray
The left lateral decubitus position X-ray is indicated in a variety of clinical conditions, including:
- Pleural effusions
- Pneumothorax
- Diaphragmatic hernias
- Gastrointestinal obstructions
- Renal calculi
This position can aid in the diagnosis of these conditions by providing a clear view of the affected structures.
Contrast agents may be used in conjunction with left lateral decubitus position X-rays to enhance diagnostic accuracy. For example, contrast agents can be used to Artikel the gastrointestinal tract, making it easier to identify obstructions.
Technical Considerations
The optimal X-ray beam angulation and exposure parameters for left lateral decubitus position imaging are as follows:
- The X-ray beam should be directed perpendicular to the patient’s chest.
- The exposure parameters should be adjusted to minimize patient motion and optimize image quality.
Specialized equipment, such as grids and collimators, can be used to improve image clarity by reducing scatter radiation and limiting the X-ray beam to the area of interest.
Reporting and Interpretation
When interpreting left lateral decubitus position X-rays, radiologists look for the following key findings:
- The size, shape, and position of the heart and mediastinum
- The presence of any pleural effusions or pneumothorax
- The position of the diaphragm
- The presence of any gastrointestinal obstructions
- The presence of any renal calculi
Radiologists also consider the patient’s clinical history and physical examination findings when interpreting these images.
Left lateral decubitus position X-rays have some limitations. For example, this position may not be suitable for patients who are unable to lie on their side or who have severe respiratory distress.
Query Resolution
What is the purpose of a left lateral decubitus position x-ray?
The left lateral decubitus position x-ray is used to evaluate thoracic and abdominal structures, particularly to detect pleural effusions, pneumothorax, and other thoracic abnormalities.
How is a patient positioned for a left lateral decubitus position x-ray?
The patient is positioned lying on their left side, with their right arm raised above their head and their left arm resting at their side. The patient’s body should be parallel to the x-ray table, and their head should be supported by a pillow.
What anatomical landmarks are visible in a left lateral decubitus position x-ray?
Visible anatomical landmarks include the ribs, lungs, heart, diaphragm, and abdominal organs.